Unit 3 Sections 5-7
Welcome to the World of Booleans and Conditionals!
- Lesson Overview: 3.5 - Boolean Expressions
- Lesson Overview: 3.6 - Conditionals
- Analyzing Code Walkthrough
Lesson Overview: 3.5 - Boolean Expressions
- Here we will focus on:
- basics of Booleans
- its relationship with binary
- relational operators
- Logical Operators
What is a boolean?
- A data type with two possible values: true or false
Boolean and Binary
So similar yet so different.
- Boolean math and binary notation both use the same two ciphers: 1 and 0.
- However, please note that Boolean quantities are restricted to a singlular bit (can only be either 1, or 0)
- On the otherhand, binary numbers may be composed of many bits adding up in place-weighted form to any finite value, or size
Must Knows
- A Boolean value is either TRUE or FALSE
- The AP Exam will provide you with a reference sheet with the operators below.

- A few ways these operators could be used...

- With the grades below, use a boolean expression to determine if the average grade is above an 80 and print the result (True or False)
- Try it in as few steps as possible!
- Be creative! There are obviously TONS of different practical solutions
gradeList = [90, 65, 60, 75, 95]
averageGrade = sum(gradeList)/len(gradeList)
if averageGrade > 80:
print("The average grade is: " + averageGrade + "%")
else:
print("The average grade is below 80%.")
print("100 == 100:",100==100)
print("Hello == Adios:","greeting"=="farewell")
print("Hello != Adios:","greeting"!="farewell")
print("Hello == Hola:","greeting"=="greeting")
print("5>=4:", 5>=4)
print ('')
# Notice that relational operators can even work on lists!
# For lists, the relational operator compares each respective component until an answer is derived
print("['a','b','c'] > ['x','y','z']:", ['a','b','c'] > ['x','y','z'])
print("[1,2,3,5] > [1,2,3,4]:", [1,2,3,5] > [1,2,3,4])
print("[1,2,3,5] < [1,2,3,4]:", [1,2,3,5] < [1,2,3,4])
print("[1,2,3,5] == [1,2,3,4]:", [1,2,3,5] == [1,2,3,4])
Logical Operators!
These types of operators don't necessarily deal with equivalent/non-equivalent values, but they rather work on operands to produce a singular boolean result
- AND : returns TRUE if the operands around it are TRUE
- OR : returns TRUE if at least one operand is TRUE
- NOT : returns TRUE if the following boolean is FALSE
print("1 > 2 or 5 < 12:", 1 > 2 or 5 < 12)
# Output TRUE using OR ^
# Output FALSE using NOT
print("24 > 8:", not 24 > 8)
# Output FALSE using AND
print("10 > 20:", 10 > 20 and 20 < 10)
x = 20
y = 10
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
x = 20
y = 10
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
else:
print("x is not greater than y")
num1 = 100
num2 = 150
sum = num1 + num2
# you could just do
# print(sum)
# because if it's 200 it'll print 200 anyways lol
if sum == 200:
print(200) # or just print(sum)...
else:
print(sum)
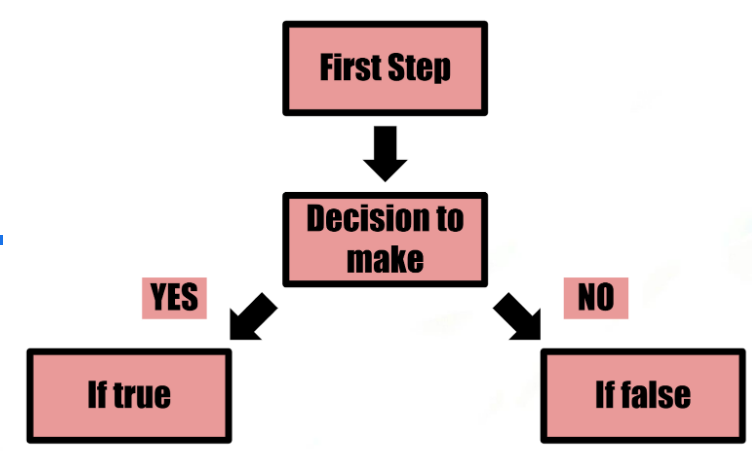
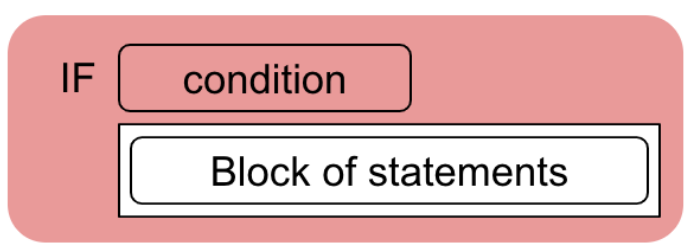
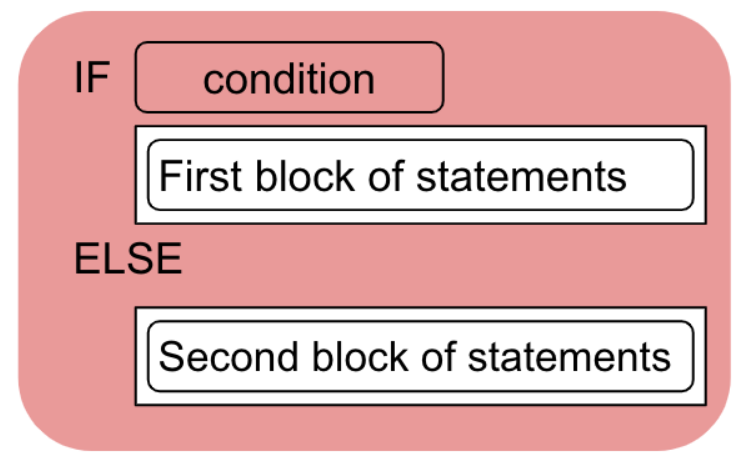
- Nested conditional statements consist of conditional statements within other conditional statements
- Utilizes "if else" statements within "if else" statements
- Basics of a nested conditional:
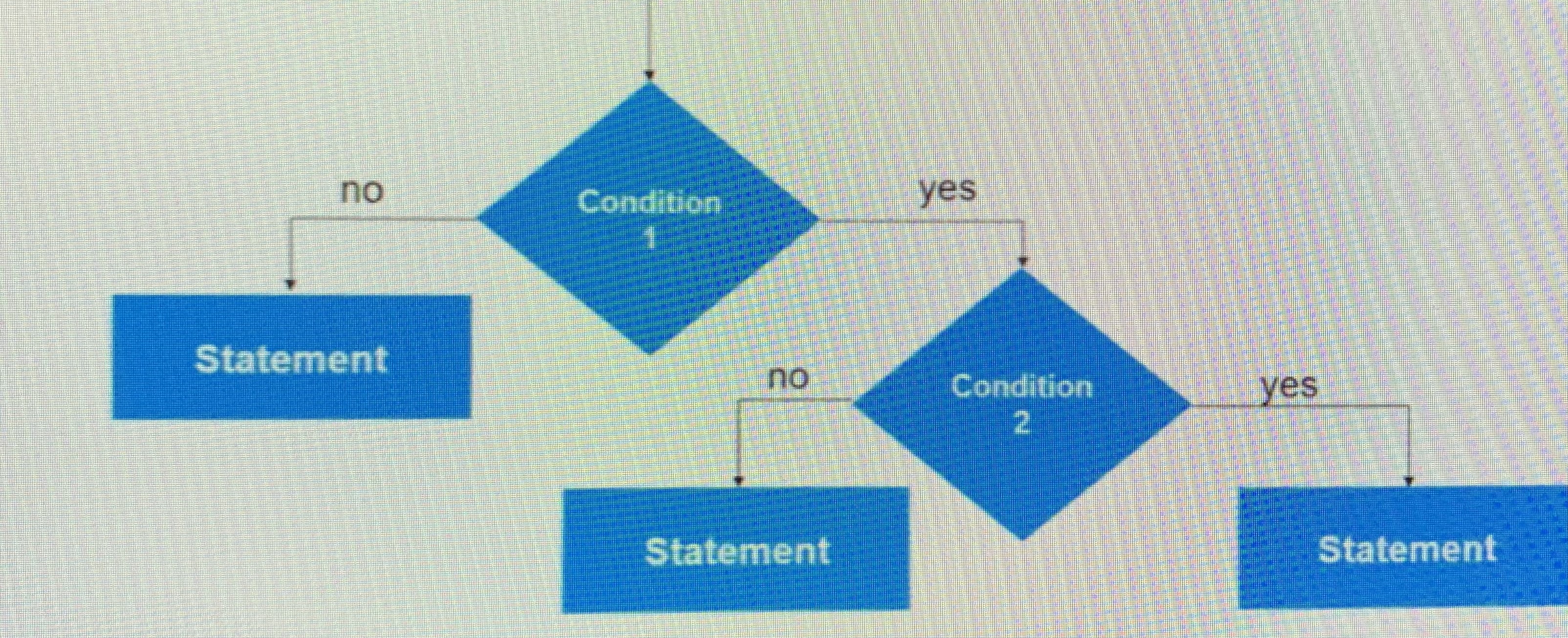
- Block Coding Visual of Nested Conditionals:
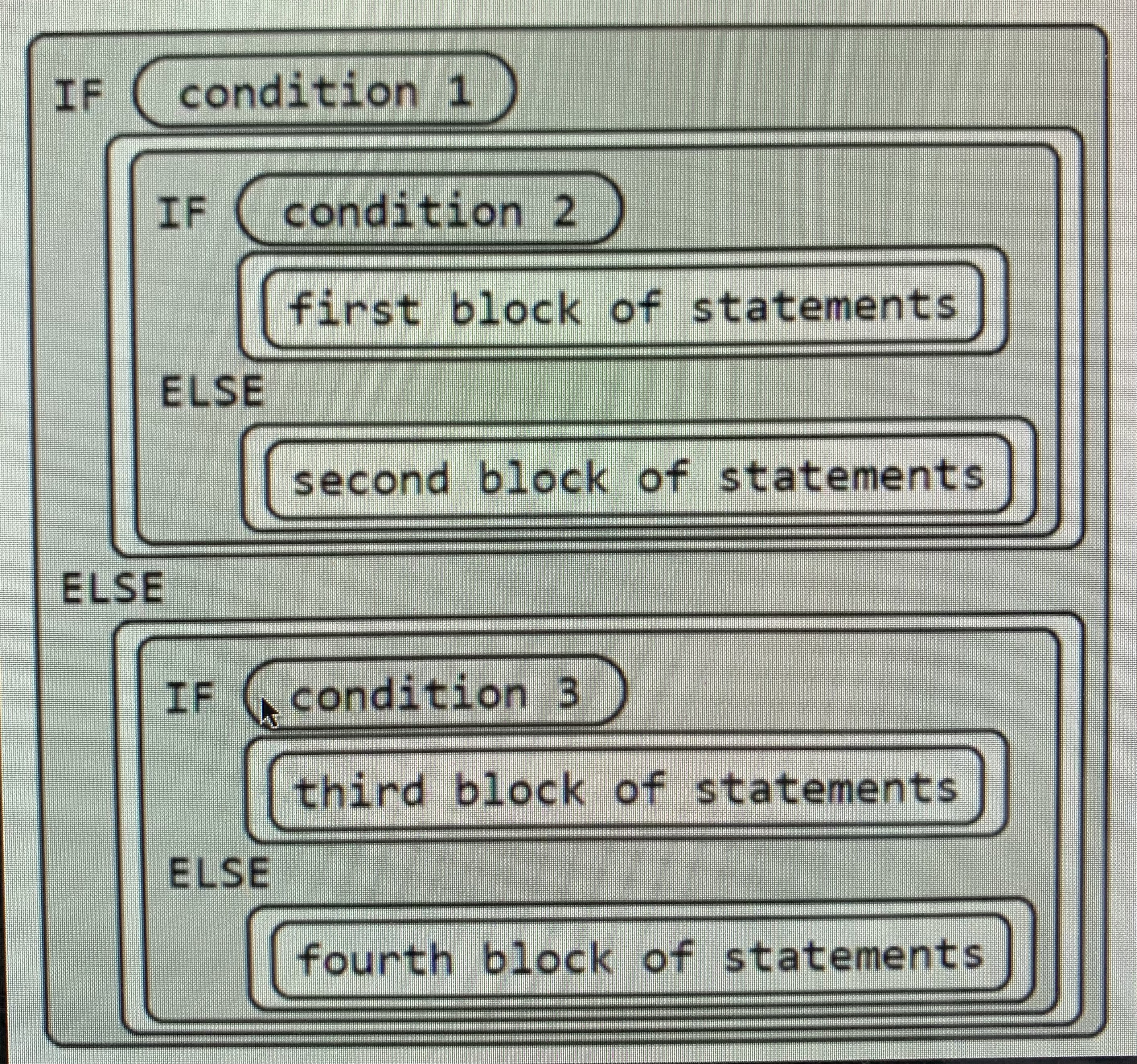
- Example Psuedocode of Nested Conditional Statements

Analyzing Code Walkthrough
- Psuedocode to the left, block code to the right
-
Approach the problem by going through each condition one at a time
- Decide which ones are false to skip and which ones are true to execute
-
You Try:

score = 82
if (score >= 90)
{
console.log("You got an A, congrats!")
}
else
{
if (score >= 75)
{
console.log("Please come to retake up to a 90 next week at tutorial!")
}
else
{
console.log("You have detention!")
}
}
protein = 25
carbs = 36
sugar = 11
if (carbs >= 55 || protein <= 20 || sugar >= 15)
{
console.log("Your lunch is too unhealthy, please pick a new one")
}
else
{
if (carbs < 35 || protein < 25)
{
console.log ("This lunch is alright but try to add some more carbs or protein")
}
else
{
if (sugar >= 11)
{
console.log ("Looks great but lets see if we can cut down on sugar, we don't want diabetes!")
}
else
{
console.log ("Amazing, you created a healthy lunch!!!")
}
}
}
Writing Nested Code Activity
- Write a program that fits these conditions using nested conditionals:
- If a person has at least 8 hours, they are experienced
- If a person is experienced their salary is 90k, if they have ten hours or above their salary 150k
- If a person is inexperienced their salary is always 50k
- print the salary of the person at the end and whether they are experienced or not
var hrs = 10
var salary = ""
var experienced = true
if (hrs >= 10) {
salary = "150k"
}
else if (hrs >= 8) {
salary = "90k"
}
else {
salary = "50k"
experienced = false
}
console.log("This person has...\n" + "Salary: " + salary + "\n" + "Experience: " + experienced)
Hacks Assignments:
Conditionals:
- Write a program that fits these conditions using nested conditionals:
- If the product is expired, print "this product is no good"
- If the cost is above 50 dollars, and the product isn't expired, print "this product is too expensive"
- If the cost is more than 25 dollars but under 50, and the product isn't expired, print "this is a regular product"
- If the cost is under 25 dollars, print "this is a cheap product"
product = {"expired":false, "cost":10}
if (product["expired"] == true) {
console.log("This product is no good!!!!!!!")
}
else {
if (product["cost"] > 50) {
console.log("THis product is too expensive!11111")
}
else if (product["cost"] > 25) {
console.log("this product normal")
}
else {
console.log("cheap")
}
}
Boolean/Conditionals:
- Create a multiple choice quiz that ...
- uses Boolean expressions
- uses Logical operators
- uses Conditional statements
- prompts quiz-taker with multiple options (only one can be right)
- has at least 3 questions
- Points will be awarded for creativity, intricacy, and how well Boolean/Binary concepts have been intertwined
qAndA = {
"question" : ["What language was this quiz coded in?", "sus amognsu", "what do you think of kanye"],
"answers" : [["python","english","java","javascript"], ["among us","sussy baka","among among","agmosnus"], ["great","ok","meh","no good"]],
"correct" : ["a", "b", "d"],
"letters" : ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
}
totalQs = len(qAndA["question"])
i = 0
score = 0
while i != totalQs:
qAnswered = False
currentQ = qAndA["question"][i]
print(currentQ + "\n")
n = 0
while n < 4:
print(str(qAndA["letters"][n]) + ": " + str(qAndA["answers"][i][n]))
n += 1
ans = input(currentQ)
ans.lower()
print("")
while qAnswered == False:
if ans == "a" or "b" or "c" or "d":
if ans == qAndA["correct"][i]:
score += 1
print("correct!11111")
else:
print("NO")
qAnswered = True
else:
print("Enter a valid letter option (a, b, c, or d)")
print("you score is: " + str(score) + "\n")
i += 1